METAL INJECTION MOLDING
WHAT IS METAL INJECTION MOLDING?
Metal Injection Molding (MIM), is a manufacturing process that utilizes an injection molding technique similar to the plastic injection technology, but instead of using plastic materials (polypropylene, polyamide, polyethylene, polycarbonate, etc.) uses a metal/thermoplastic feed stock to create components with complex geometries for a fraction of the cost of other manufacturing technologies (machining, stamping, casting, etc.)
LEARN ABOUT METAL INJECTION MOLDING!
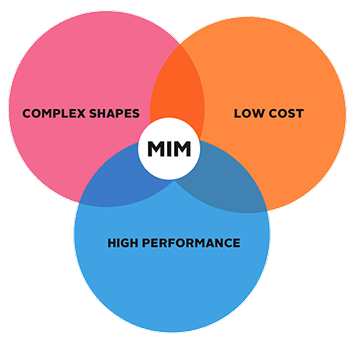
MIM TECHNOLOGY ALLOWS TO GET THE BEST PERFORMANCE COMPONENTS WITH COMPLEX GEOMETRY FOR A FRACTION OF THE TRADITIONAL PRODUCTION COST.
THE METAL INJECTION MOLDING PROCESS
Metal Injection Molding (MIM), sometimes referred to as Powder Injection Molding, combines the technical aspects and competitive advantages of plastic injection molding with powdered metallurgy.
Metal Injection Molding combines the strength and durability of metal with the flexibility inherent in the injection molding process. Metal Injection Molding is a highly cost effective method for producing a wide variety of components and is an excellent alternative to other forms of metal working such as die-casting, investment casting and many forms of machining. Typically, ideal parts for MIM are small in size and range in weight from .1 grams to 450 grams. Complex geometries, tight tolerances, high density and exceptional repeatability are some of the characteristics that make Metal Injection Molding the go-to process for metal parts production in a variety of industries.
FEEDSTOCK FORMULATION AND MIXING
Metal powders are mixed with thermoplastic polymers and waxes (binder) using heat to form a mixture in which every metal particle is uniformly coated. Once the mixture cools, it’s granulated to form the feedstock for the injection molding machines.
ARC has the capability of creating our MIM feedstocks in house, which allows us to produce high quality materials quickly and in a controlled environment. Our expertise in compounding materials for Metal Injection Molding allows us to maintain absolute consistency to eliminate defects in the molding process. We are able to create custom blends for specific applications.
Metals commonly used for MIM parts include:
Low alloy steels
Stainless steels
High-speed steels
Irons
Cobalt alloys
Copper alloys
Nickel alloys
Tungsten alloys
Titanium alloys
For a complete list of MIM Materials and properties see the MIM Materials Properties data sheet.
metal powder.
MOLDING
Feedstock is heated and injected into a mold using modified conventional mold presses. This produces a “green” part which is about 20% larger than the finished version. ARC has a wide variety of molding machines including electric, hydraulic and hybrid machines that range from 17 – 500 tons of clamping force.
DEBINDING
Debinding is the process of removing a portion of the binding additives from the molded parts prior to sintering. This creates a pathway for the remaining binders to exit the part during sintering. ARC uses both thermal and chemical debinding units for this process. The equipment is automatically controlled and monitored. Our chemical debinding units have solvent recovery capability which decreases the impact to the environment as well as lowering replacement solvent costs.


SINTERING
During sintering, the parts are heated in a furnace to remove the remaining binders and fuse together the metal particles. ARC uses conventional vacuum furnaces as well as custom furnaces to ensure the parts achieve the highest density. This allows ARC to consistently demonstrate highly repeatable quality metrics that our customers have come to expect.


